- Mon-Sat (9am - 5pm)
- Aditi_aggi@yahoo.com
- +91-7982047515
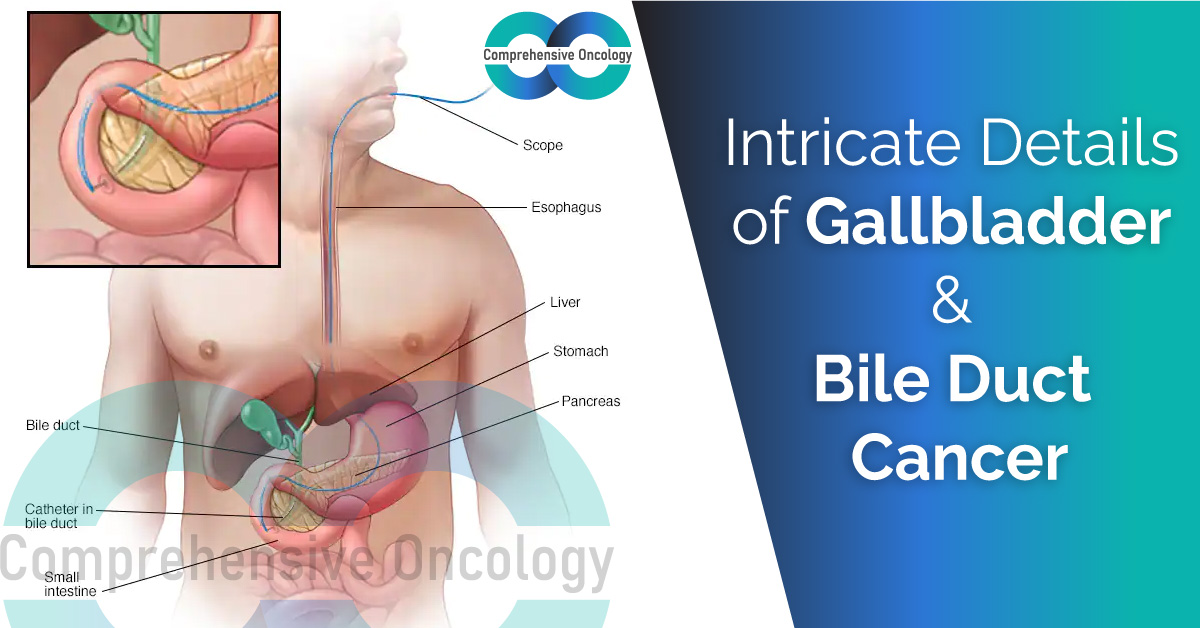
The bile duct and gallbladder are linked. They are frequently linked to diseases that affect one of them and conditions that affect the other organs
Cholangiocarcinoma, or bile duct cancer, is rare cancer that develops in the bile ducts, which transport bile from the liver or gallbladder to the small intestines. This form is most common in adults over 50, but it can happen at any age.
Unfortunately, there is no known way to avoid most bile duct tumors. We do not influence many established risk factors for bile duct cancer, such as age, race, and bile duct anomalies. There are, however, a few things you may do to lower your risk.
One key strategy to minimize one's risk of bile duct cancer and many other types of cancer is achieving and maintaining a healthy weight. According to the experts, people should try to keep a healthy weight, stay physically active, and follow a healthy eating pattern that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while limiting or avoiding red and processed meats, sugary drinks, and highly processed foods.
People may also be able to minimize their risk of bile duct cancer by doing the following
Gallbladder carcinoma is a rare disease. And if they are identified early on, the chances of survival are excellent; nevertheless, in most cases, the condition is discovered later on when the prognosis is often inferior.
The majority of gallbladder malignancies have no known cause. Many recognized gallbladder cancer risk factors, such as age, gender, race, and bile duct abnormalities, are not in our control. You can reduce your risk by following some steps.
Because gallstones are a substantial risk factor, removing the gallbladders of everyone with gallstones could avert numerous malignancies. On the other hand, gallstones are very frequent, and gallbladder cancer is sporadic even in persons with gallstones. Most doctors do not advocate removing the gallbladder unless the gallstones create issues. These cancers are often detected at an advanced stage as their symptoms are non specific and often treated for long time for gallstones.
If your symptoms do not resolve after conservative/medical treatment, please meet an expert and get a proper evaluation done for the cause. Gall bladder and bile dust cancers have a much better outcome if they are detected early.
Treatment for these cancers is mostly surgical if they are detected at an early stage. And may need some further treatment depending on the surgical specimen report in form of radiation or chemotherapy. This plan is best decided after thoroughly evaluating the complete case and as per the patients general physical condition.
Dr. Aditi Aggarwal has worked in radiation oncology for ten years, treating patients with thoracic cancer, gastrointestinal cancer, bone and soft tissue cancer, gynecological cancer, breast cancer, and neurological cancers.
As a medical doctor, Dr. Aditi Aggarwal holds an MBBS degree from Lady Hardinge Medical College Delhi, a MD degree in radiation oncology from VMMC and Safdarjang Hospital Delhi, as well as a post-doctoral diploma in cancer research from Catalyst Clinical Sciences in Pune.
Cancer is usually classified into four stages, with stage 0 being the earliest stage and stage IV being the most advanced. The stage of a cancer is an important factor in determining the prognosis and the best treatment options. Here's a brief overview of the different stages of cancer:
Stage 0: This is the earliest stage of cancer, and it refers to cancer that is still in its original place and has not spread to other parts of the body. It is also known as carcinoma in situ.
Stage I: This stage means that the cancer is still small and has not spread to other parts of the body. It may be treatable with surgery or other local treatments.
Stage II: At this stage, the cancer is larger and may have spread to nearby lymph nodes. It may be treated with surgery and/or radiation therapy, or other systemic treatments such as chemotherapy.
Stage III: This stage means that the cancer has spread to nearby tissues or organs and/or to distant lymph nodes. Treatment may involve a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, and/or systemic treatments such as chemotherapy.
Stage IV: This is the most advanced stage of cancer, and it means that the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, such as the liver, lungs, bones, or brain. Treatment at this stage is typically palliative, meaning that it aims to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life, rather than cure the cancer.
It's important to note that the staging of cancer can vary between different types of cancer and different systems used to classify the stages. Your healthcare provider can give you more information specific to your situation.
There is no single vaccine that can prevent or cure all types of cancer. However, some vaccines can help prevent certain viral infections that can increase the risk of certain cancers, such as the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine, which can help prevent HPV-related cancers such as cervical, vaginal, vulvar, and anal cancer.
Additionally, some cancers can be treated with a type of immunotherapy called cancer vaccines, which help stimulate the body's own immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. These vaccines are still in the experimental stage and are only available through clinical trials.
However, there are many things you can do to reduce your risk of developing cancer, such as eating a healthy diet, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding tobacco products, and getting regular cancer screenings. Your healthcare provider can give you more information on how to reduce your risk of cancer.
The symptoms of cancer can vary depending on the type and part of the body of cancer, as well as its stage. Some common symptoms of cancer include:
It's important to keep in mind that these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions, and not all of them are present in all cases of cancer. If you are experiencing any symptoms that are new or persist for a long time, it's important to talk to your healthcare provider to determine the cause and get appropriate medical attention. Early detection and treatment of cancer can often lead to better outcomes.
Through us, you can schedule a Dr. Aditi Aggarwal priority appointment. Request a callback or dial 7982047515 to reach us.