- Mon-Sat (9am - 5pm)
- Aditi_aggi@yahoo.com
- +91-7982047515

First step in treatment for any cancer is making a diagnosis of the disease, which needs a biopsy in most of the cases and then some investigations, to understand where all in the body the cancer has spread. This determines the stage of the cancer.
After this, the specialist will decide the right treatment for them based on the stage and kind of cancer, they have alongside other medical conditions and as per patients age and general condition.
If individuals have cancer, then they can consult with a practitioner who specializes in the department of Radiation Oncology.
Radiation Oncology is the branch of oncology where patients are treated with radiation therapy.
Radiation treatment acts by treating patients using high energy X Rays that cause the tumor cells to be killed and growth of cells is stopped , thus controlling/curing the cancer. This happens as X rays cause damage of the DNA (genetic material) of cells , thus stopping them from division.
It is a local therapy and would affect the area where radiation is directed at and does not affect other areas in the body.
Radiation is most efficient at destroying tissues that are actively growing. Cancer tissues are more vulnerable to this therapy because of a couple of reasons. Such as
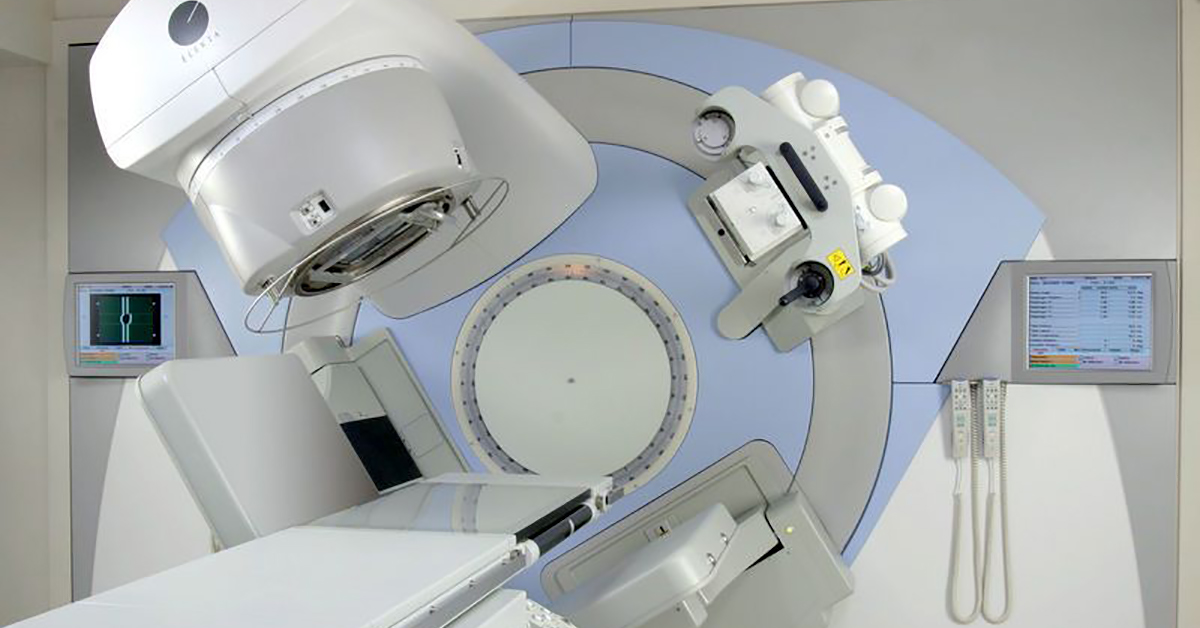
After treatment decision for Radiation has been taken, strategizing the plan is done.
The individual will first go through the simulation scan (radiation planning scan) with the assistance of an advanced CT scanner. Oral or iv contrast can be utilized. A device is required to keep the individual motionless, the mould or cast is made at the appointment for a simulation scan. This is required to make sure the patient is in same position on every treatment and radiation is focussed.
The radiation oncologist then outlines the parts to be treated, such as the tumour, and the parts staying away from, such as the vital organs. This therapy strategy is arranged and monitored by a radiation oncologist, medical physicists, and dosimetrists. The Radiation therapy then goes through safety and quality checks.
Once approved by the radiation Oncologist, the patient is taken up for treatment on machine by the Radiotherapy Technician..
Radiation oncology is performed on the medical facilities treatment unit under the supervision of the radiation oncologist. The radiation therapist, and other medical care team members involving radiation technicians, dietitians, and nurses, will observe the patient during treatment to handle the side effects.
The entire process of radiation planning as well as treatment is an absolutely painless procedure, done on an OPD basis. Patients undergoing radiation and continue to work or do their routine activities.
If the patient is receiving Radiation therapy to treat a cancerous tumour, the doctors can have them undergo regular scans after their treatment to monitor how their cancer has reacted to Radiation Oncology. In some instances, their cancer can react to the therapy right away. In other cases, it can take several weeks and even months for their cancerous tumour to respond. In those cases, the entire medical team of ours, monitors the patient tirelessly to help them out.
Dr. Aditi Aggarwal has worked in radiation oncology for ten years, treating patients with thoracic cancer, gastrointestinal cancer, bone and soft tissue cancer, gynecological cancer, breast cancer, and neurological cancers.
As a medical doctor, Dr. Aditi Aggarwal holds an MBBS degree from Lady Hardinge Medical College Delhi, a MD degree in radiation oncology from VMMC and Safdarjang Hospital Delhi, as well as a post-doctoral diploma in cancer research from Catalyst Clinical Sciences in Pune.
Cancer is usually classified into four stages, with stage 0 being the earliest stage and stage IV being the most advanced. The stage of a cancer is an important factor in determining the prognosis and the best treatment options. Here's a brief overview of the different stages of cancer:
Stage 0: This is the earliest stage of cancer, and it refers to cancer that is still in its original place and has not spread to other parts of the body. It is also known as carcinoma in situ.
Stage I: This stage means that the cancer is still small and has not spread to other parts of the body. It may be treatable with surgery or other local treatments.
Stage II: At this stage, the cancer is larger and may have spread to nearby lymph nodes. It may be treated with surgery and/or radiation therapy, or other systemic treatments such as chemotherapy.
Stage III: This stage means that the cancer has spread to nearby tissues or organs and/or to distant lymph nodes. Treatment may involve a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, and/or systemic treatments such as chemotherapy.
Stage IV: This is the most advanced stage of cancer, and it means that the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, such as the liver, lungs, bones, or brain. Treatment at this stage is typically palliative, meaning that it aims to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life, rather than cure the cancer.
It's important to note that the staging of cancer can vary between different types of cancer and different systems used to classify the stages. Your healthcare provider can give you more information specific to your situation.
There is no single vaccine that can prevent or cure all types of cancer. However, some vaccines can help prevent certain viral infections that can increase the risk of certain cancers, such as the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine, which can help prevent HPV-related cancers such as cervical, vaginal, vulvar, and anal cancer.
Additionally, some cancers can be treated with a type of immunotherapy called cancer vaccines, which help stimulate the body's own immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. These vaccines are still in the experimental stage and are only available through clinical trials.
However, there are many things you can do to reduce your risk of developing cancer, such as eating a healthy diet, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding tobacco products, and getting regular cancer screenings. Your healthcare provider can give you more information on how to reduce your risk of cancer.
The symptoms of cancer can vary depending on the type and part of the body of cancer, as well as its stage. Some common symptoms of cancer include:
It's important to keep in mind that these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions, and not all of them are present in all cases of cancer. If you are experiencing any symptoms that are new or persist for a long time, it's important to talk to your healthcare provider to determine the cause and get appropriate medical attention. Early detection and treatment of cancer can often lead to better outcomes.
Through us, you can schedule a Dr. Aditi Aggarwal priority appointment. Request a callback or dial 7982047515 to reach us.